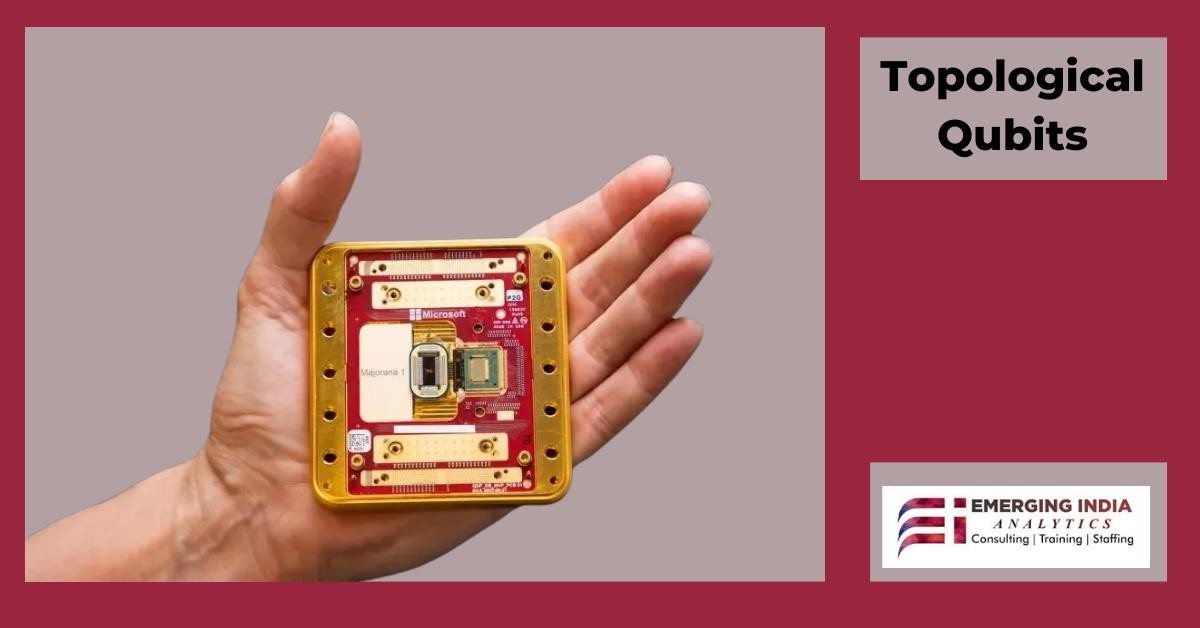
Quantum computing is no longer a distant dream—it’s rapidly becoming a reality, promising to revolutionize industries by solving problems far beyond the capabilities of classical computers. Microsoft has made a groundbreaking move with Majorana 1, a next-generation quantum chip that could redefine computational power, supercomputing, and cryptography. But what sets Majorana 1 apart from other quantum processors? How does it compare to existing quantum and classical computing models?
In this blog, we’ll uncover the science behind Majorana 1, its role in the future of computing, and how it could reshape industries from AI to cybersecurity. If you’re curious about the future of quantum technology, this is a must-read!
Understanding Majorana 1
As the race to achieve practical quantum computing intensifies, Microsoft has introduced a game-changing innovation: Majorana 1. This cutting-edge quantum chip is designed to address one of the biggest challenges in quantum computing—stability and error correction. Unlike traditional quantum processors, which rely on superconducting qubits, Majorana 1 is built using topological qubits, a novel approach that significantly enhances coherence, fault tolerance, and computational efficiency.
One of the key obstacles in scaling quantum technology is the high susceptibility of qubits to decoherence and noise, which leads to computational errors. Conventional quantum processors require extensive error correction algorithms, making them harder to scale. However, topological qubits—the foundation of Majorana 1—offer intrinsic error resistance, reducing the need for complex error correction mechanisms. This not only improves stability and reliability but also paves the way for the development of large-scale quantum computers that can outperform classical systems in solving complex problems.
With Majorana 1, Microsoft is taking a bold step toward the realization of a truly scalable and commercially viable quantum computing ecosystem. If successful, this breakthrough could revolutionize industries ranging from cryptography and artificial intelligence to pharmaceutical research and materials science. The potential applications are vast, and as quantum technology advances, we may soon witness a new era of supercomputing power that reshapes the technological landscape.
What Makes Majorana 1 Unique?
1) Topological Qubits
Topology in this context refers to a branch of mathematics that deals with properties of space that remain unchanged under continuous deformations (like stretching or twisting, but not tearing). In quantum computing, topological qubits use this concept to protect quantum information in a way that makes them more robust against errors.
How Topology Helps in Quantum Computing
- Error Resistance: Unlike traditional qubits (like superconducting qubits) that are highly sensitive to noise, topological qubits encode information in non-local quantum states, making them less prone to decoherence.
- Majorana ZeroModes: Microsoft’s Majorana 1 approach relies on Majorana fermions, exotic quasiparticles that obey non-Abelian statistics. These particles exist at the edges of certain materials and can be used to create qubits that are naturally protected from external disturbances.
- Braiding Operations: The key feature of topological qubits is “braiding“, where quantum information is stored in the topological properties of the system rather than in specific quantum states. This makes operations on qubits more stable and less susceptible to environmental noise.
Advantages of Topological Qubits in Majorana 1
- More Stable: Since quantum information is stored in a topological manner, it is less affected by local perturbations.
- Lower Error Rates: Traditional qubits require error correction mechanisms, but topological qubits are inherently protected.
- Scalability: Because of their robustness, topological qubits could make large-scale quantum computing more feasible.
How Do Topological Qubits Work?
At the heart of topological qubits are Majorana fermions, theoretical quasiparticles that exhibit non-abelian statistics, meaning their quantum state depends on the order in which they are manipulated. This unique property enables a more fault-tolerant and stable computational environment, reducing susceptibility to external noise.
Unlike traditional qubits, where information is stored in a single location, topological qubits distribute quantum information across multiple entangled states in a topological phase of matter. This means that even if one part of the system is disturbed, the overall quantum state remains intact—effectively implementing intrinsic error correction at the hardware level.
Key Elements That Make Topological Qubits Unique
- Majorana Fermions: These exotic quasiparticles emerge in certain topological superconductors and serve as the building blocks of topological qubits. They enable a form of topological protection, making qubits inherently resistant to local noise.
- Braiding Operations: Instead of directly measuring quantum states (which often collapses them), computations are performed by “braiding” Majorana fermions around one another. This non-abelian process makes quantum operations robust against errors.
- Topological Superconductors: Special materials engineered to host Majorana fermions. These superconductors support exotic quantum states that enable fault-tolerant computations.
- Intrinsic Error-Correction: Unlike classical quantum computers that require extensive software-based error correction, topological qubits have hardware-encoded protection against decoherence, leading to higher computational stability.
- Scalability for Industrial Applications: With a reduced need for active error correction, Majorana 1 can pave the way for scalable quantum computing suitable for commercial, cryptographic, and AI-driven applications.
By leveraging Majorana fermions and topological protection, Microsoft’s Majorana 1 chip is positioned as a potential breakthrough in fault-tolerant quantum computing, bringing us one step closer to practical, large-scale quantum systems.
2) Microsoft’s Unique Approach
While companies like Google and IBM have made significant strides in quantum computing using superconducting qubits, Microsoft is betting on a radically different approach—topological quantum computing. Unlike traditional quantum processors that require extensive error correction algorithms, Microsoft’s Majorana 1 leverages topological qubits, which naturally resist noise and decoherence, leading to greater stability and scalability.
This shift is more than just a technical upgrade; it represents a fundamental transformation in quantum hardware architecture. By focusing on Majorana fermions and their unique braiding properties,
Microsoft is working towards a fault-tolerant quantum system that could be more practical for real-world industrial applications, from cryptography and AI to drug discovery and materials science.
How Majorana 1 Compares to Other Quantum Chips
| Feature | Majorana 1 | Google Sycamore | IBM Eagle |
| Qubit Type | Topological Qubits | Superconducting Qubits | Superconducting Qubits |
| Error Rate | Lower | Higher | Higher |
| Scalability | More Scalable | Requires Heavy Error Correction | Limited Scalability |
| Computational Power | High | High | Moderate |
| Industrial Use Potential | High | Medium | Medium |
Google’s Sycamore made headlines when it demonstrated quantum supremacy, completing a computation in seconds that would take a classical supercomputer thousands of years. However, it still struggles with noise, error correction, and scalability, making it less viable for long-term commercial use.
Similarly, IBM’s Eagle has made progress in quantum volume, but its reliance on superconducting qubits means it faces the same limitations of error-prone operations and limited stability.
In contrast, Microsoft’s Majorana 1 offers a fundamentally more resilient architecture. By harnessing the power of Majorana fermions and topological protection, it minimizes quantum noise and reduces the need for complex error correction protocols. This makes it a strong candidate for scalable, fault-tolerant, and commercially viable quantum computing—potentially setting the stage for practical quantum applications in fields like cybersecurity, optimization, and artificial intelligence.
With Majorana 1, Microsoft isn’t just refining existing quantum computing techniques—it’s redefining the entire approach, paving the way for a more robust, scalable, and powerful quantum future.
How Majorana 1 Can Change the World
Quantum computing has the potential to redefine technology, revolutionize industries, and unlock solutions to problems that were previously unsolvable. With Majorana 1, Microsoft is pushing the boundaries of computational power, stability, and scalability, bringing us closer to real-world quantum applications that could transform global industries.
Here’s how Majorana 1 could reshape the future:
1. Pharmaceuticals & Drug Discovery
The process of developing new drugs and vaccines takes years due to the complexity of molecular simulations. Quantum computing, powered by topological qubits, could accelerate drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions at an unprecedented speed and accuracy. This means:
✔ Faster discovery of life-saving treatments
✔ More precise protein folding analysis for diseases like Alzheimer’s & cancer
✔ Improved personalized medicine based on genetic data
2. Cryptography & Cybersecurity
While quantum computers pose a threat to classical encryption, Majorana 1 could pioneer quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring a secure digital future. With fault-tolerant quantum encryption, we could:
✔ Develop post-quantum cryptography to safeguard sensitive data
✔ Enhance blockchain security against quantum attacks
✔ Secure financial transactions, national security, and global communications.
3. AI & Climate Modeling & Sustainability
Predicting climate change is an incredibly complex computational challenge. Current supercomputers struggle with the massive datasets required for detailed climate models. Majorana 1’s computational power could:
✔ Provide hyper-accurate climate predictions
✔ Optimize carbon capture & renewable energy solutions
✔ Help governments make data-driven environmental policies
4. AI & Machine Learning
Quantum-enhanced artificial intelligence could lead to breakthroughs in deep learning, optimization, and natural language processing. With Majorana 1, we could see:
✔ Faster neural network training for AI models
✔ Improvements in real-time decision-making (finance, healthcare, robotics)
✔ Enhanced quantum AI applications for automation and self-learning systems
5. Material Science & Energy Solutions
Quantum computing could revolutionize material design and energy production, helping industries discover superconductors, battery technologies, and nuclear fusion breakthroughs. With Majorana 1, we could:
✔ Develop room-temperature superconductors, reducing global energy waste
✔ Optimize solar panel efficiency & energy storage
✔ Unlock nuclear fusion, providing limitless clean energy
6. A New Era of Quantum Computing
With its topological qubits, error-resistant architecture, and unparalleled computational power, Majorana 1 isn’t just an evolution—it’s a revolution. Microsoft’s quantum breakthrough has the potential to reshape industries, solve global challenges, and push humanity into the next technological frontier.
Are we witnessing the dawn of practical quantum computing? Only time will tell, but one thing is certain—Majorana 1 is a game-changer.
How Majorana 1 Will Impact Supercomputers
Supercomputers, despite their immense power, still rely on classical architectures with limitations in processing massive amounts of data efficiently. Majorana 1 could serve as a quantum accelerator, providing a hybrid quantum-classical computing environment that:
- Enhances problem-solving capabilities
- Reduces time complexity for difficult calculations
- ImprovesAI training by exponentially speeding up large-scale data analysis
With companies like Microsoft, IBM, and Google racing toward practical quantum applications,
Majorana 1 positions Microsoft as a front-runner in integrating quantum computing with traditional supercomputing.
The Road Ahead: What to Expect from Majorana 1
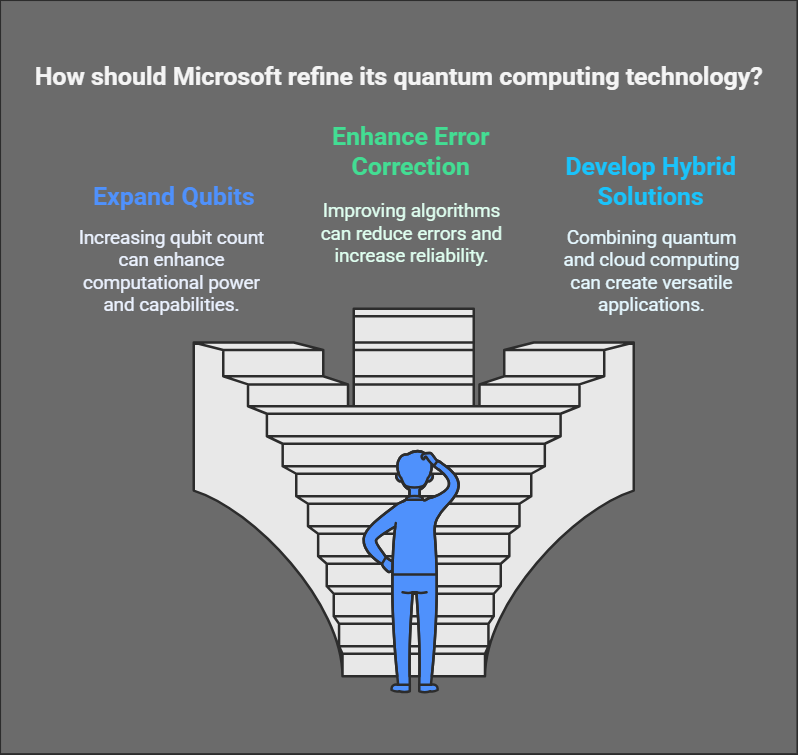
Although Majorana 1 is a significant breakthrough, quantum computing is still in its infancy. Microsoft aims to refine its technology by:
- Expanding the number of qubits
- Enhancing error correction algorithms
- Developing hybrid quantum-cloud computing solutions
The ultimate goal is to achieve a fault-tolerant quantum computer that surpasses the limitations of today’s classical supercomputers. With continued research, we may soon witness a future where quantum computing becomes an integral part of industries worldwide.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s Majorana 1 chip is a groundbreaking step toward making practical quantum computing a reality. It overcomes stability and scalability challenges by leveraging topological qubits, setting a new standard in the field.
From drug discovery and AI advancements to quantum-resistant cybersecurity and climate modeling, Majorana 1 has the potential to transform industries and push computational boundaries beyond what was ever thought possible.