Features
- Lectures - 74
- Duration – 36 Weeks
- Case Studies and Assessment – 5+
- Delivery Mode- Online/Offline
- Batches- Weekends
- Capstone Projects- 10+ Projects
Cybersecurity is one of the most searched terms in the current generation. Cyber security may be defined as the practice of defending the system, networks, programs, and vital information of a person or any organization from continuously increasing malicious threats and cyber-attacks. Cybersecurity experts use various methods and technologies to put a stopper to such kinds of attacks and safeguard the information.
With each passing day, Cyber criminals are becoming more and more equipped and sophisticated. So, the rate of intrusion is increasing rapidly and all organizations are showing concern about the safeguarding of their data this is the reason the Cybersecurity domain is experiencing huge growth and demand. The Bureau of Labor Statistics has predicted a whooping growth of 28% in the domain of Information security between the years 2016-2026 and it’ll be opening a larger scope for information security analysts or cyber security specialists.
Program Overview
- The most comprehensive curriculum with training material designed by NASSCOM, along with its 35 SIG(Special Interest Group) members such as Goldman Sachs, IBM, Ins Analytics, Infosys BPO, Insights of Data, JP Morgan, Karvy Analytics, Knod Global, KPMG, Wipro, WNS, Wells Fargo, Amazon, Capgemini, Concentrix, CITI, Cyient Insights, Accenture, EXL, First America, Fractal Analytics, GENPACT, Google, ADP Deloitte, HCL, HDFC, IBM, ISC2, NIIT University, PwC, Symantec, TCS to name a few, that will prepare you for future externalities in the data analytics industry and fulfill the gap of academics and industry requirements.
This official NASSCOM-CERTIFIED Cyber Security Program covers all the demanded tools of Cyber Security which includes Python, Java, AWS, OWASP, Burp Suite, Snort, Wireshark, MetaSploit, and many more.
Program Structure
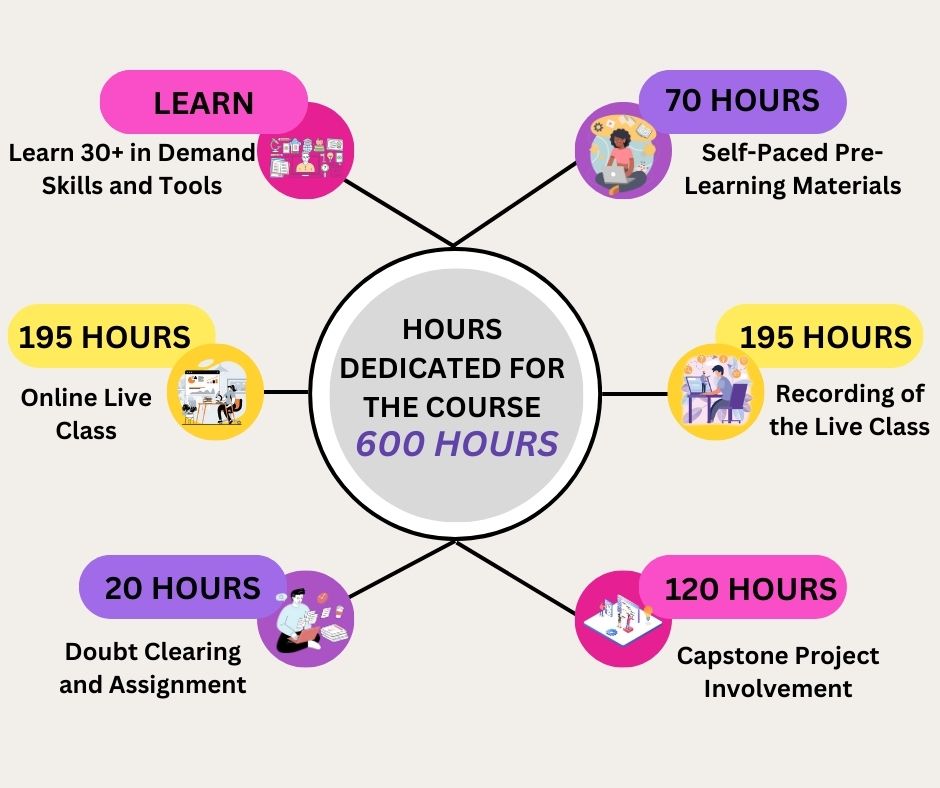
This Nasscom Certified Security Analyst program will cover in-depth knowledge and will give proficiency in more than 80 tools and skills to undertake any problem efficiently on the organizational level. This course will help the learner to lead a successful career in the field of cyber security. This sophisticatedly designed 600 Hours cybersecurity curriculum has been bifurcated into five different segments to help the learner grasp everything smoothly.
- 70 hours Pre-Learning: Before you come in, get ready for the Program. You will get a series of online recorded tutorials to understand the structure of cybersecurity
- 195 hours Program: Here, you will get Hands-on Experience with various Cyber Security tools and techniques which include Python, Kali Linux, Java, Beautiful Soup, Nmap, Samba, IAM, LDAP, CAPTCHAS, DDos Attack, Botnet Attack, SQL Injection, Hashing, Encryption, Firewall, Metasploit, Packet Inspection, ICMP Attack, Vulnerability Management, Indian Cyberspace and Laws, Cyber Security Framework, CIA and many more.
- 335 hours Post Program: Learning does not stop here. After completing the Program, you will work on Projects and assignments. Doubt clearing is also provided. You will be working on any one capstone project from the list of a few projects of your choice. You also will get the recording of the live classes.
Eligibility:
This cyber security program has been curated carefully to ensure the smooth learning of the enrolled candidates. It will help the learners to match the various hierarchical requirements of various organizations working in the cybersecurity domain. It’ll help the learner to know the current world scenario, demand and need of cyber security, and, use of various tools to solve problems.
-
- Work Experience – This program will help the senior and mid-senior level managers of the cybersecurity domain to make efficient decisions for the organization. This course can also be opted by any young or mid-level IT professionals looking for a transition into the domain of cyber security. A fresh graduate of any stream wants to join the cyber security domain and start a career. It can be a choice for any senior professional involved actively in the cyber security practices of any organization.
- Education – Graduates from Engineering/ Mathematics / IT backgrounds or any equivalent stream can join the program
Sample Certificate

Nasscom Certificate-

-
Module 1 : Python and Linux
(Chapter 1: Introduction to Python and Linux)Introduction to Python, Conditional Statement, Variables, Data Types, Data Structures, Functions, Requests, OS, Exception Handling, File Handling. Numpy, Pandas, What is Machine Learning?, Types of Machine Learning, Scikit Learn, What is Natural Language Processing?, Stop Words, Tokenization, Lemmatization, NLTK Library, Introduction to Attributes, Scrapy Installation, Spider Building with Scrapy, Xpath, Beautiful Soup / Selenium, Installation and Scrapping, Twisted, nmap, Pymetasploit, Mechaniz, Cryptography Library, Basics of Linux, File Permission, Ownership, editors, ftp, Apache, samba, nfs, Shell scripting.
-
Module 2 : Information Security and Attacks
(Chapter 2: Introduction - Cyber Security Fundamentals)What is Hacking?, Computer Security Threats, Goals of Ethical Hacking, Skills and Tools required for Ethical Hackers, Process of Ethical Hacking, Process of Ethical Hacking - Demonstration Part 1, Process of Ethical Hacking - Demonstration Part 2, Information Gathering Concepts, Foot Printing, Reconnaissance, Active Passive Scanning, CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity & Availability) Threat, Vulnerabilities, Threat Actor, Risk etc, Definitions & Concept, Advanced Cyber Security - Threats and Governance, What are Threats?, Types of Threats (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Breach, DOS, Elevation of Privilege),GitHub DDos Attack, Types of Attack (DOS, Phishing, Ransomware), Introduction and importance to Information Security, Elements of Information Security (Purpose, Audience and Scope, Security Objective-CIA, Authority and Access Control, Data Classification (level 1-5), Support and Operation, Security Awareness, Responsibilities Rights and Duty. Principle of Information Security (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability), Introduction to Data Security, Types of Data Security (Encryption, Data Erasure, Data Masking, Data Resiliency), Data Security Strategy (Physical Security of Servers and User Devices, Access Management and Controls, Backups).
-
Chapter 3: Web Technologies, OWASP, DVWA, Bwapp with practicals
Practical on Metasploit and bwap, bWAPP Features, Why should you learn bWAPP?, bWAPP Prct. Dvwa Feature and Use, Kali Linux (tool) Demonstration - Web Application Attack: Broken Authentication, Demonstration - Web Application Attack: Blind SQL Injections, Demonstration - Web Application Attack: Cross Site Scripting, Web Application Domain, Web Application Domain: Common Attacks, Hacking Methodology, Mobile Application Domain, Mobile Application Domain: Types of Android Attacks, Steps of Incident Preventation, Network Reconnaissance Incidents (Host Detection, Port Enumeration, Vulnerability Assessment), DoS, Malicious Code, 02. Information Security and Attack Chapter 03 Web Technologies, OWASP, DVWA, Bwapp with Practicals, Information Gathering (Spyders, Robots and Crawlers/Search Engine Discovery/Reconnaissance/Testing Web Application Fingerprint/. Analysis of Error Codes:)
-
Chapter 4: Cryptography with Practicals
Remediation Planning, Encryption, What is Encryption?, Prerequisites for Encryption, How does Encryption work?, Vulnerability Assessment, What is Decryption?, Encryption Vs Decryption, Types of Encryption, Encryption Algorithms and Protocols, Web Application Architecture, Web Application Attacks, Web Server Architecture, Web Server Attacks
-
Chapter 5: Network Concepts
Introduction to Information Security Controls, Types of Controls (Organizational Control, People Control, Physical Control, Technological Control), Preventive, Corrective and Digestive Control, OSI Concept, Protocols, ARP, SMTP, ICMP, TCP, 3 Way Handshaking, Security Market Outlook, Computer Networks - Architecture, Layered Architecture, Open Systems Interconnect (OSI) Model, Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), Network Scanning, Enumeration, Common Network Threats/Attacks, Packet Inspection, Deep Packet Inspection(Intrusions Detection System and Intrusion Prevention, System), IP Security, ICMP Attacks. TCP and UDP Security. Attacking Availability: Denial-of-Service, Attacks, Distributed DOS Attacks, SSL/TLS Data/Application Security: Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability, Authorization, Authentication, Identification, Non-Repudiation, Types of Control (Preventive, Detective, Corrective, Deterrent, Recovery, Compensating), Access Control, Security Vulnerability Management, Network Devices (Hub, Switch, Router, Bridge, Gateway, Modem, Repeater, Access Point), Configuration of Network Devices, Network Configuration Tool, Firewall, Firewall Configuration,
-
Chapter 6: Device Log Correlation, Data Management, DLP, Data backup
Introduction to Data Leakage (Direct Losses and Indirect Losses.), Types of Data Leakage, NPI (e.g. Customer Data), Confidentiality Info, PHI (e.g. Patient's Records), Intellectual Property, Data Leak Vector :- HTTP, Email, Networked Printer, End Point, Internal Mail, IM, Webmail, Data Classification, Types of Data Classification, Steps and Process of Data Classification, Content Awareness, Content Analysis Techniques (Rule Based, Data Based Finger Printing, Partial Document Matching, Lexicon), DLP (Data in Motion, Data in Rest, Data in Use), DLP Limitation, DLP using DRM, DEFINITION OF EVENT CORRELATION, EVENT CORRELATION USE CASES AND TECHNIQUES, BENEFITS OF EVENT CORRELATION, Event Log, Key Concept of Log Management (log, event, incidents), Log Management Process and Challenges, Configuration of Windows Event Log, SIEM, Remote Software Access, Web Proxies, Firewall, Routers, What is Data Backup?, Importance of Data Backup, Why to Backup?, RPO, RTO, Types (Mirror, Full, Differential, incremental Backup, Cloud Backup, FTP Backup,), Storage Types (Local or USB Disks, Network Shares and NAS, Data Backup to Tapes, Cloud Storage), Backup Procedures.
-
Chapter 7: ISO, ISMS, Compliance, Risk Management
Information Security Policy, Top Information Security Threats (Unsecure or Poorly Secured Systems, Social Media Attacks, Social Engineering, Malware on Endpoints, Lack of Encryption, Security Misconfiguration, Active and Passive Attack, Cyber Security Regulations, Roles of International Law, The State and Private Sector in Cyberspace, Cyber Security Standards. The INDIAN Cyberspace, National Cyber Security Policy 2013, Elements of an Information Security Policy (Purpose, Scope, Objective, Authorization and Access Control, Classification, Data Support Operation, Security Standard and Guideline (COSO, COBIT, ITIL, NIST, NSA, ISO, IT Act, Copyright, Patent law, IPR), Laws of Indian Govt, Cyber Security Landscape Cyber Security Policy Management , Cyber Security Policy Ecosystem, Cyber Security Policy Management Design, Cyber Security Frameworks, ISMS Environment, Frameworks, ISO27001 Standard, Security Metrics, Types of Security Metrics (Strategic Security Metrics, Security Management Metrics, Operational Security Metrics), Mean-Time-to-Detect and Mean-Time-to-Respond, Number of Systems with Known Vulnerabilities, Number of SSL Certificates Configured Incorrectly, Volume of Data Transferred using the Corporate Network, Number of Communication Ports Open During a Period of Time, Frequency of Review of Third-Party Accesses, Frequency of Access to Critical Enterprise Systems by Third Parties, Percentage of Business Partners with Effective Cybersecurity Policies. Introduction to Risk Assessment, Identification of Risk Assessment, Risk Assessment Model (Identification, Assessment, Mitigation, Preventation), Role and need of Risk Assessment.
-
Chapter 8: Information Security Management – Roles and Responsibilities
Hierarchy of Information Security (Board of Director, CIO, CISO, CEO, System Architect, System Engineer, Security Director, System Admin, Security Analyst, IS Auditor, DB Admin), Importance of Information Security Policy, Element of Information Security (Purpose, Audience, CIA, Encryption Policy, Data Backup Policy,
-
Module 3 : Configuration and Incident Handling
(Chapter 9: Incident Handling Concepts)Incidents, Types of Incidents, Impact of Incidents, Information (Alert,Logs, Network Flow), Phases of Incident Handling, Incident Response Life Cycle
-
Chapter 10: Security Devices, Security configuration & Management, Sniffing concepts, Network attacks with practicals
Firewall, Why Firewall?, DMZ, Troubleshooting Cisco IOS Firewall, Troubleshooting Routers, Anti Virus and Anti Spam Ware, Incident Response Process (identification, Recording, Response, Communication, Containment, Classification, Investigation), Unauthorized Access Incidents, Traffic Filtering (NAT-Network Address Translation, VPN- Virtual Private Network, IDP-Intrusion Detection & Prevention, CISCO IOS Firewall IDS Configuration Initializing Cisco IOS Firewall IDS, Initializing the Post Office, Configuring and Applying Audit Rules, Verifying the Configuration), IPS configuration, IPS Tuning, SNMP Configuration, Configuration of MoD Security, Patch Management (Windows Server Update Services)
-
Module 4 : Security Audit
(Chapter 11: Vulnerability Assessment with Practicals)What is Vulnerability?, Need of Vulnerability, Types of Vulnerability Assessment (Host Assessment, Network and Wireless Assessment, Database Assessment, Application Scans, Active, Passive, Internal, External), Vulnerability Assessment Process, Vulnerability Classification (Misconfigurations), Default Installations, Buffer Overflows, Unpatched servers, Default Passwords, Open Services, Application Flaws, Open System Flaws, Design flaws), Demonstration - SQL Injection, WordPress Plugin SQL Vulnerability, Buffer Overflow & Vulnerabilities Case Study: WhatsApp Attack, VA tools (Nmap, Nessus, Whisker, Enum. Firewalk)
-
Chapter 12: Penetration Testing, Explotations(Web, Windows, Linux) Practicals and Report writing & Documentation
Configuration Management, Server, Server Hardening, Server and Attack Prevention, SecCM Planning, Penetration Testing, CM Tools (Solar Wind),Benefits of Configuration Management,
-
Chapter 13: Information Gathering (Active & Passive) with Practical
What is and Why Penetration Testing, Stages (Pre attack, Attack Phase, Post Attack), Planning and Reconnaissance, Scanning, Gaining Access, Maintaining Access Analysis, SIEM, SySLog, Social Engineering
-
Chapter 14: Malware, Virus, Worms etc and Password Hacking with Practicals
SQL Injection Threat, Malware, Password Attack, Zero-Day Attack), Virus, Worm, Trojan, What are Vulnerabilities?, Vulnerability Categorization, SQL Injection Anatomy, Cross Site Scripting Anatomy.
-
Chapter 15: Information Security Audit
Information Security Audit, What is IT Security Audit?, Scope of Audit, Benefits and Types of Audit (Approach Based, Methodology Based (Penetration Tests, Compliance Audits, Risk Assessments, Vulnerability Tests, Due Diligence Questionnaires), Case Studies of Security Audit, Conduct an IT security Audit using (Metasploit Framework, OWASP), Phases of Audit, Audit Methodology, Role, Responsibility, Skills, Ethics of Auditor, 4 Phases of Information Gathering, What is Internal and External Security Audit and their Steps, Firewall Security Audit, Types of Firewalls, Intrusion Detection System, ISD security Audit Steps, Social Engineering Audit.
-
Module 5 : CAPSTONE PROJECT
Keylogger Software, Network Traffic Analyser, Password Analyser and many more